Recently i’ve published:
Etherify – bringing the ether back to ethernet
Etherify 3 – the PI 4’s dirty little secret
Etherify 4 – back to earth with “normal” ethernet hardware
please read these articles first, before reading this one.
Etherify 4 used ethernet interfaces from two air-gapped laptops connected together via ethernet to transmit information via radio.
Etherify 5 uses two Linksys LGS318 switches connected together. The intra-switch link speed is changed via SNMP via the etherify5.sh script. Changing the speed to 100Mbit/s results in a detectable signal around 50MHz, while changing to 10Mbit/s turns off this signal.
This demonstrates that network devices can also be used to exfiltrate data from air-gapped networks. The particular network device and port can be selected based upon being close to an attacker, or having hardware that radiates more etc (such as out-of-spec ethernet cables).
Other frequencies might yield a better signal, however 50MHz was near amateur radio frequencies, and was selected because i already had antennas and other equipment for this band. The frequency is dependent on the actual hardware being used, always check a wide band of frequencies, previously i’ve found strong enough signals in the 125MHz-625MHz range (this extends it down to 50MHz, and probably lower).
Modulation is done via slow morse code (QRSS CW).
Transmit setup
Two Linksys LGS318 connected via ports 17 using a 1m ethernet cable were used to transmit.

192.168.1.251 uses a default factory config.
The 192.158.1.252 has autonegotiation on the transmitting port disabled (port 17):
config-file-header switcheca015 v1.1.1.9 CLI v1.0 set system @ voice vlan oui-table add 0001e3 Siemens_AG_phone________ voice vlan oui-table add 00036b Cisco_phone_____________ voice vlan oui-table add 00096e Avaya___________________ voice vlan oui-table add 000fe2 H3C_Aolynk______________ voice vlan oui-table add 0060b9 Philips_and_NEC_AG_phone voice vlan oui-table add 00d01e Pingtel_phone___________ voice vlan oui-table add 00e075 Polycom/Veritel_phone___ voice vlan oui-table add 00e0bb 3Com_phone______________ hostname switcheca015 snmp-server server snmp-server community public ro view Default snmp-server community private rw view Default ! interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.1.252 255.255.255.0 no ip address dhcp ! interface gigabitethernet17 speed 10 no negotiation ! exit
Receive setup
A laptop running gqrx and an usb rtl-sdr receiver was used. The gqrx output was connected via pulseaudio to DL4YHF Spectrum Lab running under wine. Spectrum Lab is used to display a high resolution spectrogram. The receiver used a 50/144/432MHz whip antenna from Yaesu FT817, because it was avaliable.
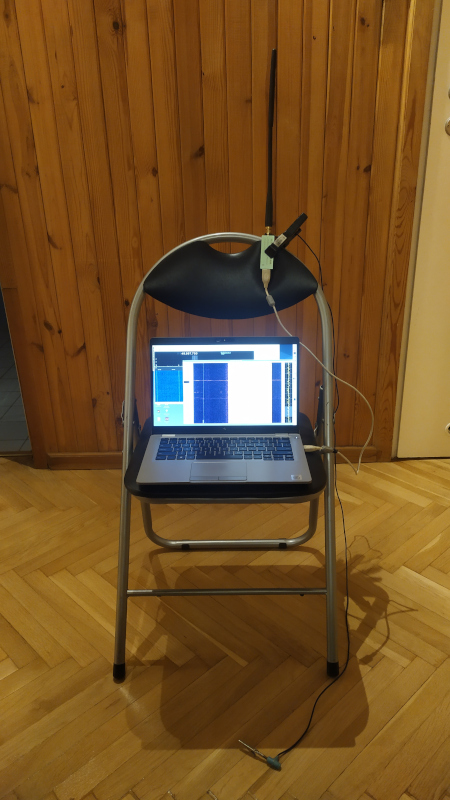

Results
Changing the interface speed will result in changing the signal radiated by the interface.
This is the signal at 5m distance at 50MHz:

The above spectrogram shows part of the message being sent (“etherify 5 demo”).
Discussion
While the previous etherify demos used Raspberry PI 4 and laptops, this shows that it is possible to run etherify from network hardware, such as an ethernet switch. The Linksys LG318 switch is not a big enterprise switch, but is pretty well designed to not cause interference (good shielding etc).
When trying this on other hardware, please check as much spectrum as possible to find the leaked signal (at least from 10MHz to 1GHz). The best frequency is not always obvious, and depends how the device generates it’s clocks internally, which frequencies will leak out more etc.
Using network infrastructure hardware enables transmission of data from an interface that is closer to the receiver, or radiates better (due to asymetry in the ethernet cable, bad hardware etc).
The “software” side is intentionally a very primitive silly hack.
Happy air-gap jumping 🙂
If you cite this, please include the webpage address and attribute Jacek Lipkowski (SQ5BPF). Email can be sent to my_callsign @ this_domain.